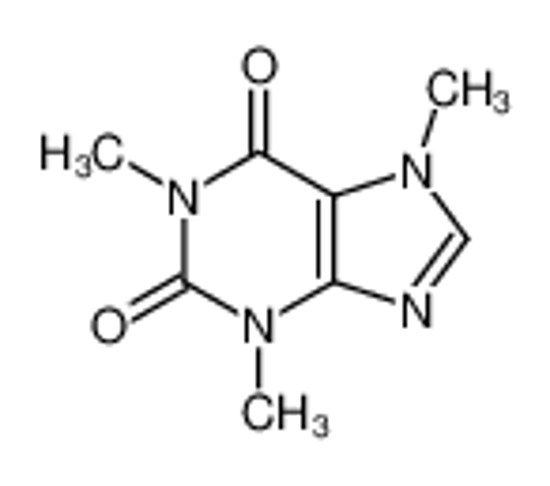
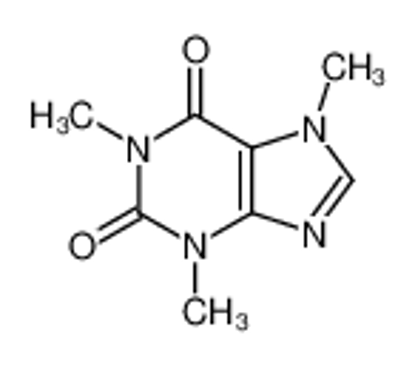
ALL CATEGORIES
Categories
- Hot Categories
-
Biochemicals and Pharmaceutical Chemicals
- Pharmaceutical Impurities
- Pharmaceutical Intermediates
-
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs)
- Cardiovascular system
- Brain and nervous system
- Gastrointestinal tract/ metabolism
- Respiratory system
- Other ATC
- Infections and infestations
- Orphan drugs
- Endocrine system
- Genitourinary system
- Skin
- Blood and blood forming organs
- Malignant disease
- Sensory organs
- Immune disease
- Muscles, bones, and joints
- Veterinary Drugs
- Biochemicals
- Pharmaceutical Excipients
- Material Chemicals
-
Electronic Chemicals
- Photonic and Optical Materials
- Liquid Crystals and Conductive Compounds
- OLED and PLED Materials
- Synthetic Tools and Reagents
- Organic Photovoltaic (OPV) Materials
- Organic Field Effect Transistor (OFET) Materials
- Electronic Chemicals for Integrated Circuits
- New Energy Batteries-related Chemicals
- Additives for Electronic and Electrical Materials
- Sublimed Materials
- Substrates and Electrode Materials
- Materials for Printing and Printed Electronics
- Paints and Coatings
- Natural Products and Extracts
-
Agrochemicals
- Pesticide Intermediates
-
Pesticides
- Herbicides
- Insecticides
- Bactericides
- Acaricides
- Plant Growth Regulators
- Nematicides
- Rodenticides
- Insect Attractants
- Hygienic Insecticides
- Molluscicides
- Herbicide Safeners
- Insect Repellents
- Algicides
- Chemosterilants
- Synergists
- Bird Repellents
- Insect Growth Regulators
- Wood Preservatives
- Nitrification Inhibitors
- Pesticide Adjuvants
- Fertilizers
- Commodity Chemicals
-
Catalysts and Additives
-
Additives and Auxiliaries
- Plastic and Rubber Additives
- Paint Additives
- Organic Extractants
- Textile Auxiliaries
- Water Treatment Agents
- Flame Retardants
- Synthetic Material Additives
- Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) Derivatives
- Polymer Additives
- Metal Processing Aids
- Surface Treatment Agents
- Electronic Industrial Additives
- Coupling Agents
- Mineral Processing Reagents and Smelting Additives
- Construction And Building Chemicals
- Oilfield Chemicals
- Pesticide Additives
- Adsorbents
- Leather Additives
- Heat Stabilizers
- Paper Additives
- Oil Additives
- Fillers
- Glass Antibacterial Agents
- Retarders
- Antishock Agents
- Catalysts
-
Additives and Auxiliaries